Elastic Net
Introduction
Often in applications, we encounter problems that require regularization to prevent overfitting, introduce sparsity, facilitate variable selection, or impose prior distributions on parameters. Two of the most common regularization functions are the l1-norm and squared l2-norm, combined in the elastic net regression model Friedman, Hastie, and Tibshirani (2010),
minimizeβ12m‖y−Xβ‖22+λ(1−α2‖β‖22+α‖β‖1).
Here λ≥0 is the overall regularization weight and α∈[0,1] controls the relative l1 versus squared l2 penalty. Thus, this model encompasses both ridge (α=0) and lasso (α=1) regression.
Example
To solve this problem in CVXR, we first define a function that
calculates the regularization term given the variable and penalty
weights.
elastic_reg <- function(beta, lambda = 0, alpha = 0) {
ridge <- (1 - alpha) / 2 * sum(beta^2)
lasso <- alpha * p_norm(beta, 1)
lambda * (lasso + ridge)
}Later, we will add it to the scaled least squares loss as shown below.
loss <- sum((y - X %*% beta)^2) / (2 * n)
obj <- loss + elastic_reg(beta, lambda, alpha)The advantage of this modular approach is that we can easily
incorporate elastic net regularization into other regression
models. For instance, if we wanted to run regularized Huber
regression, CVXR allows us to reuse the above code with just a
single changed line.
loss <- huber(y - X %*% beta, M)We generate some synthetic sparse data for this example.
set.seed(1)
# Problem data
p <- 20
n <- 1000
DENSITY <- 0.25 # Fraction of non-zero beta
beta_true <- matrix(rnorm(p), ncol = 1)
idxs <- sample.int(p, size = floor((1 - DENSITY) * p), replace = FALSE)
beta_true[idxs] <- 0
sigma <- 45
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 5), nrow = n, ncol = p)
eps <- matrix(rnorm(n, sd = sigma), ncol = 1)
y <- X %*% beta_true + epsWe fit the elastic net model for several values of λ .
TRIALS <- 10
beta_vals <- matrix(0, nrow = p, ncol = TRIALS)
lambda_vals <- 10^seq(-2, log10(50), length.out = TRIALS)
beta <- Variable(p)
loss <- sum((y - X %*% beta)^2) / (2 * n)
## Elastic-net regression
alpha <- 0.75
beta_vals <- sapply(lambda_vals,
function (lambda) {
obj <- loss + elastic_reg(beta, lambda, alpha)
prob <- Problem(Minimize(obj))
result <- solve(prob)
result$getValue(beta)
})We can now get a table of the coefficients.
d <- as.data.frame(beta_vals)
rownames(d) <- sprintf("$\\beta_{%d}$", seq_len(p))
names(d) <- sprintf("$\\lambda = %.3f$", lambda_vals)
knitr::kable(d, format = "html", caption = "Elastic net fits from `CVXR`", digits = 3) %>%
kable_styling("striped") %>%
column_spec(1:11, background = "#ececec")| λ=0.010 | λ=0.026 | λ=0.066 | λ=0.171 | λ=0.441 | λ=1.135 | λ=2.924 | λ=7.533 | λ=19.408 | λ=50.000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β1 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β2 | -0.035 | -0.035 | -0.033 | -0.030 | -0.022 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β3 | 0.379 | 0.378 | 0.376 | 0.372 | 0.362 | 0.334 | 0.267 | 0.101 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β4 | 1.812 | 1.811 | 1.809 | 1.804 | 1.790 | 1.755 | 1.666 | 1.453 | 0.983 | 0.135 |
| β5 | -0.410 | -0.409 | -0.408 | -0.404 | -0.395 | -0.371 | -0.310 | -0.169 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β6 | 0.352 | 0.352 | 0.350 | 0.346 | 0.336 | 0.309 | 0.245 | 0.082 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β7 | 0.397 | 0.397 | 0.395 | 0.392 | 0.382 | 0.358 | 0.297 | 0.152 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β8 | 0.098 | 0.098 | 0.096 | 0.093 | 0.085 | 0.064 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β9 | -0.051 | -0.051 | -0.049 | -0.046 | -0.039 | -0.020 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β10 | 0.084 | 0.083 | 0.082 | 0.079 | 0.071 | 0.051 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β11 | 1.134 | 1.133 | 1.132 | 1.128 | 1.117 | 1.090 | 1.020 | 0.853 | 0.494 | 0.000 |
| β12 | 0.092 | 0.092 | 0.091 | 0.089 | 0.082 | 0.066 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β13 | -0.428 | -0.427 | -0.425 | -0.420 | -0.408 | -0.378 | -0.301 | -0.112 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β14 | -0.113 | -0.112 | -0.111 | -0.107 | -0.096 | -0.070 | -0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β15 | -0.676 | -0.675 | -0.674 | -0.670 | -0.660 | -0.636 | -0.573 | -0.404 | -0.063 | 0.000 |
| β16 | 0.275 | 0.274 | 0.272 | 0.268 | 0.258 | 0.231 | 0.165 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β17 | -0.004 | -0.004 | -0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β18 | 0.186 | 0.185 | 0.184 | 0.180 | 0.170 | 0.144 | 0.082 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β19 | -0.517 | -0.516 | -0.514 | -0.509 | -0.497 | -0.465 | -0.387 | -0.210 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β20 | 0.761 | 0.761 | 0.759 | 0.755 | 0.745 | 0.719 | 0.656 | 0.487 | 0.109 | 0.000 |
We plot the coefficients against the regularization.
plot(0, 0, type = "n", main = "Regularization Path for Elastic-net Regression",
xlab = expression(lambda), ylab = expression(beta),
ylim = c(-0.75, 1.25), xlim = c(0, 50))
matlines(lambda_vals, t(beta_vals))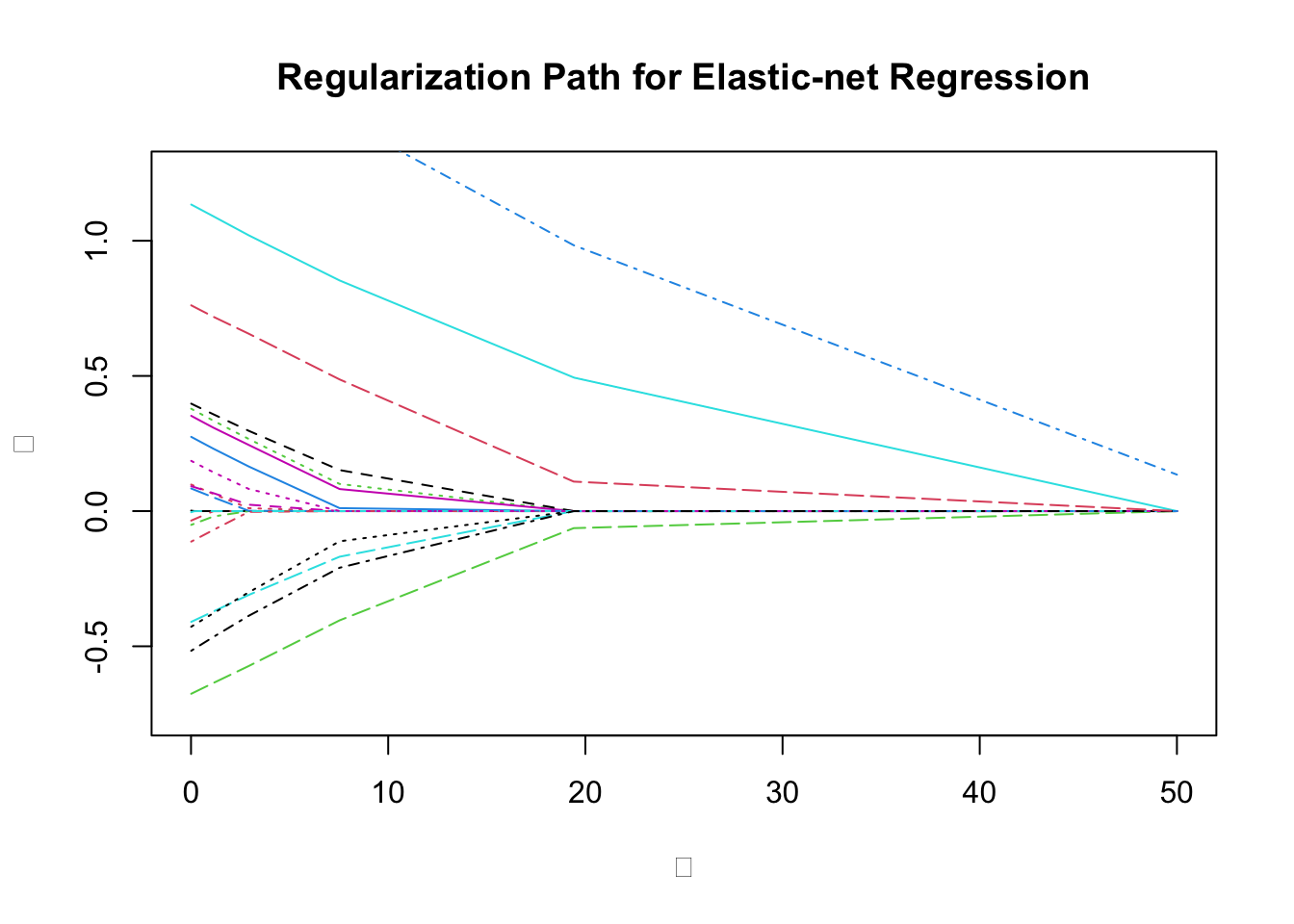
We can also compare with the glmnet results.
model_net <- glmnet(X, y, family = "gaussian", alpha = alpha,
lambda = lambda_vals, standardize = FALSE,
intercept = FALSE)
## Reverse order to match beta_vals
coef_net <- as.data.frame(as.matrix(coef(model_net)[-1, seq(TRIALS, 1, by = -1)]))
rownames(coef_net) <- sprintf("$\\beta_{%d}$", seq_len(p))
names(coef_net) <- sprintf("$\\lambda = %.3f$", lambda_vals)
knitr::kable(coef_net, format = "html", digits = 3, caption = "Coefficients from `glmnet`") %>%
kable_styling("striped") %>%
column_spec(1:11, background = "#ececec")| λ=0.010 | λ=0.026 | λ=0.066 | λ=0.171 | λ=0.441 | λ=1.135 | λ=2.924 | λ=7.533 | λ=19.408 | λ=50.000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β1 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β2 | -0.035 | -0.035 | -0.033 | -0.030 | -0.022 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β3 | 0.379 | 0.378 | 0.377 | 0.373 | 0.364 | 0.339 | 0.277 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β4 | 1.812 | 1.812 | 1.811 | 1.807 | 1.798 | 1.776 | 1.717 | 1.568 | 1.183 | 0.205 |
| β5 | -0.410 | -0.409 | -0.408 | -0.405 | -0.397 | -0.376 | -0.320 | -0.184 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β6 | 0.353 | 0.352 | 0.351 | 0.347 | 0.337 | 0.313 | 0.253 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β7 | 0.398 | 0.397 | 0.396 | 0.392 | 0.384 | 0.361 | 0.304 | 0.158 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β8 | 0.098 | 0.098 | 0.097 | 0.093 | 0.085 | 0.063 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β9 | -0.051 | -0.051 | -0.049 | -0.047 | -0.039 | -0.020 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β10 | 0.084 | 0.083 | 0.082 | 0.079 | 0.071 | 0.051 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β11 | 1.134 | 1.134 | 1.133 | 1.130 | 1.122 | 1.102 | 1.048 | 0.911 | 0.580 | 0.000 |
| β12 | 0.092 | 0.092 | 0.091 | 0.089 | 0.082 | 0.066 | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β13 | -0.428 | -0.427 | -0.426 | -0.422 | -0.411 | -0.384 | -0.315 | -0.130 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β14 | -0.113 | -0.112 | -0.111 | -0.107 | -0.097 | -0.071 | -0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β15 | -0.676 | -0.675 | -0.674 | -0.671 | -0.663 | -0.643 | -0.590 | -0.433 | -0.071 | 0.000 |
| β16 | 0.275 | 0.274 | 0.273 | 0.269 | 0.259 | 0.234 | 0.171 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β17 | -0.004 | -0.004 | -0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β18 | 0.186 | 0.185 | 0.184 | 0.180 | 0.170 | 0.145 | 0.085 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β19 | -0.517 | -0.516 | -0.514 | -0.510 | -0.499 | -0.472 | -0.400 | -0.226 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| β20 | 0.761 | 0.761 | 0.760 | 0.756 | 0.748 | 0.728 | 0.678 | 0.529 | 0.137 | 0.000 |
## Testthat Results: No output is good## Error: `beta_vals` not identical to e_net$beta_vals.
## 7/200 mismatches (average diff: 8.83e-08)
## [41] 0.001150 - 0.001150 == -1.00e-07
## [61] 0.000222 - 0.000222 == -1.50e-07
## [71] 1.127833 - 1.127833 == 1.63e-08
## [72] 0.088552 - 0.088552 == 2.15e-08
## [74] -0.106758 - -0.106758 == -1.76e-08
## [77] -0.000382 - -0.000382 == 2.65e-07
## [102] -0.000237 - -0.000237 == 4.74e-08Session Info
sessionInfo()## R version 4.4.2 (2024-10-31)
## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin20
## Running under: macOS Sequoia 15.1
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-x86_64/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
## LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.4-x86_64/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib; LAPACK version 3.12.0
##
## locale:
## [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
##
## time zone: America/Los_Angeles
## tzcode source: internal
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices datasets utils methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] glmnet_4.1-8 Matrix_1.7-1 kableExtra_1.4.0 ggplot2_3.5.1
## [5] CVXR_1.0-15 testthat_3.2.1.1 here_1.0.1
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] gtable_0.3.6 shape_1.4.6.1 xfun_0.49 bslib_0.8.0
## [5] lattice_0.22-6 Rmosek_10.2.0 vctrs_0.6.5 tools_4.4.2
## [9] generics_0.1.3 tibble_3.2.1 fansi_1.0.6 highr_0.11
## [13] pkgconfig_2.0.3 desc_1.4.3 assertthat_0.2.1 lifecycle_1.0.4
## [17] compiler_4.4.2 stringr_1.5.1 brio_1.1.5 munsell_0.5.1
## [21] gurobi_11.0-0 codetools_0.2-20 htmltools_0.5.8.1 sass_0.4.9
## [25] cccp_0.3-1 yaml_2.3.10 gmp_0.7-5 pillar_1.9.0
## [29] jquerylib_0.1.4 rcbc_0.1.0.9001 clarabel_0.9.0.1 Rcplex_0.3-6
## [33] cachem_1.1.0 iterators_1.0.14 foreach_1.5.2 tidyselect_1.2.1
## [37] digest_0.6.37 stringi_1.8.4 slam_0.1-54 dplyr_1.1.4
## [41] bookdown_0.41 splines_4.4.2 rprojroot_2.0.4 fastmap_1.2.0
## [45] grid_4.4.2 colorspace_2.1-1 cli_3.6.3 magrittr_2.0.3
## [49] survival_3.7-0 utf8_1.2.4 withr_3.0.2 Rmpfr_0.9-5
## [53] scales_1.3.0 bit64_4.5.2 rmarkdown_2.29 bit_4.5.0
## [57] blogdown_1.19 evaluate_1.0.1 knitr_1.48 Rglpk_0.6-5.1
## [61] viridisLite_0.4.2 rlang_1.1.4 Rcpp_1.0.13-1 glue_1.8.0
## [65] xml2_1.3.6 pkgload_1.4.0 osqp_0.6.3.3 svglite_2.1.3
## [69] rstudioapi_0.17.1 jsonlite_1.8.9 R6_2.5.1 systemfonts_1.1.0